testicular torsion vs epididymitis test|testicular torsion vs epididymitis signs : bespoke A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of epididymitis, or the inflammation of the epididymis (i.e., duct running behind the testes). Conversely, a negative Prehn's sign is . WEBLike thousands of players who use VegasSlotsOnline.com every day, you now have instant access to over 7780 free online slots that you can play right here. You can play our free slot games from anywhere, as long as you’re connected to the internet. You don’t need to bet real money, you can play our free online slot machines 24/7 with no .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Cbet is a leading online platform for sports betting, casino games, live casino, and esports. Join now and enjoy the best odds, bonuses, and promotions in Canada.
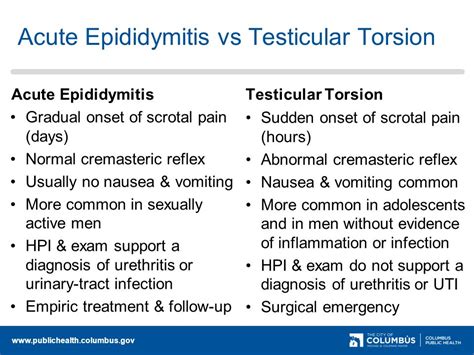
A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of epididymitis, or the inflammation of the epididymis (i.e., duct running behind the testes). Conversely, a negative Prehn's sign is .Acute epididymitis is diagnosed when there is increased blood flow on dynamic images and increased uptake around the region of the epididymis, while testicular torsion as decreased . Testicular isotope scanning can differentiate epididymitis, which results in “hot spots” caused by increased perfusion near the affected testicle, from testicular torsion, which results in .
what's a soft shoulder new york permit test
Testicular torsion and acute epididymitis are a major subject and can be identified in the majority of cases by medical history taking, clinical examination and scrotal ultrasound. . This presentation helps differentiate epididymitis and orchitis from testicular torsion, which is a surgical emergency. Typical physical findings include a swollen, tender epididymis or testis. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the .Ultrasonography is noninvasive and can help to differentiate epididymitis from testicular torsion. [7, 8] (The ultrasonogram below reveals the presence of epididymitis.) One topic of study is.
Epididymitis is managed medically, whereas testicular torsion is a surgical emergency. This activity reviews the presentation, evaluation, and management of .
Doctors suspect epididymitis or epididymo-orchitis based on a physical examination. They'll usually also do: A urine test to look for infection. Sometimes, ultrasound, to be sure that you . The presence of pyuria is consistent with epididymitis, orchitis, or urinary tract infection but does not rule out the possibility of testicular torsion. Treatment / Management. Ultrasound is not a perfect test for testicular torsion, especially in the very young. For example, 40% of neonatal testicles may have no apparent color flow Doppler.Immediate urologic consultation should be obtained if testicular torsion cannot be clearly differentiated from epididymitis or other scrotal pathology. In a 21-year retrospective study of 252 pediatric patients with diagnosed epididymitis or epididymo-orchitis, age at first presentation was 10.92 ± 4.08 years.
Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity.The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis.Investigation and treatment. Colour Doppler sonography is indicated in equivocal cases, but has operator-dependent factors that can cause variances in sensitivity (86–100%) and specificity (95–100%). 3,8–10 Importantly, a normal investigation does not rule out testicular torsion if history and examination indicate otherwise. In children, the use of ultrasonography should not . The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. If ultrasound with color Doppler shows lower blood flow to a testicle than is typical, the testicle is twisted. If blood flow is higher than typical, this can help confirm that you have epididymitis.Testicular torsion causes your testicle to twist and cuts off its blood supply. It causes severe pain and requires emergency care. . What tests will be done to diagnose testicular torsion? Your healthcare provider may order a scrotal ultrasound to determine if blood is flowing within your testicular tissues. A scrotal ultrasound is a quick .
Testicular torsion in newborns and infants. Testicular torsion can occur in newborns and infants, though it's rare. The infant's testicle might be hard, swollen or a darker color. Ultrasound might not detect reduced blood flow to the infant's scrotum, so surgery might be needed to confirm testicular torsion. Treatment for testicular torsion in .
This topic also addresses the clinical management of testicular torsion. Further detail on evaluation and management of necrotizing fasciitis and acute epididymitis are discussed separately. Traumatic injury to the male external genitalia, including the scrotum, is also discussed separately: (See "Necrotizing soft tissue infections".)For men with severe unilateral pain with sudden onset, those whose test results do not support a diagnosis of urethritis or urinary tract infection, or for whom diagnosis of acute epididymitis is questionable, immediate referral to a urologist for evaluation for testicular torsion is vital because testicular viability might be compromised.Testicular torsion is an emergency. It requires immediate referral to a surgeon . (appendix testis), epididymitis and testicular torsion; . Blood tests, ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound are not useful in the acute setting; Once testicular torsion and irreducible hernia have been confidently excluded, ultrasound may be considered if the .
If testicular torsion is present, the testicle must be detorted and orchiopexy performed as soon as possible for fertility to be maintained. . Testicular torsion versus epididymitis: a diagnostic challenge Pediatr Emerg Care. 1992 Dec;8(6):347-50. doi: 10.1097/00006565-199212000-00011. Authors E M Petrack 1 , W Hafeez. Affiliation 1 Division .
Testicular torsion and acute epididymitis are a major subject and can be identified in the majority of cases by medical history taking, clinical examination and scrotal ultrasound. Suspicion of testicular torsion is an indication for urgent surgical exploration. Acute scrotum pain is defined as “the constellation of new-onset pain, swelling, and/or tenderness of the intrascrotal contents.” Patients may describe the onset of symptoms as rapidly as occurring within minutes or up to 1 to 2 days, dependent on the etiology. The acute scrotum is an umbrella term that includes a wide variety of unique disease processes. Rapid .
Introduction. Acute scrotal pain commonly presents on unilaterally and encompasses a wide array of potential differentials, including testicular torsion and epididymitis.. All cases should be approached thoroughly, as the risk of misdiagnosis (especially in cases of torsion or malignancy) are sizeable.. In this article, we discuss how to approach .The appendix testis is a small appendage of normal tissue that is usually located on the upper portion of the testis. The appendix epididymis is a small appendage on the top of the epididymis (a tube-shaped structure connected to the .A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes). Doctors suspect epididymitis or epididymo-orchitis based on a physical examination. They'll usually also do: A urine test to look for infection. Sometimes, ultrasound, to be sure that you don't have a .
SUPPORT/JOIN THE CHANNEL: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCZaDAUF7UEcRXIFvGZu3O9Q/join My goal is to reduce educational disparities by making education FR. Epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis; see the image below) is a significant cause of morbidity and is the fifth most common urologic diagnosis in men aged 18-50 years. Epididymitis must be differentiated from testicular torsion, .Testicular torsion. Testicular tumor. Testicular cancer. What is the difference between epididymitis and orchitis? Epididymitis refers to inflammation of the tube at the back of your testicle. Orchitis is when your testicle itself swells. These conditions sometimes occur at the same time. When this happens, healthcare providers call it . Prehn’s test is used to differentiate testicular pain caused by acute epididymitis and testicular torsion. The test involves elevating the testes to assess the impact on testicular pain. A reduction in testicular pain is associated with epididymitis. Although this test can provide some clinical value it is inferior to Doppler ultrasound when .
which diagnostic test is used for detecting soft-tissue lesions
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . Granberg CF, DaJusta DG, Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic Test for Testis Torsion in Pediatric Acute Scrotum: A Prospective Comparison to Gold Standard . Color Doppler ultrasonography is the test of choice for immediate evaluation of scrotal masses. . A retrospective review of pediatric patients with epididymitis, testicular torsion, and torsion . 1. Background. Torsion of spermatic cord is a urologic emergency. It is the most important acute scrotal abnormality that needs a fast diagnosis for surgical exploration (1-3).Ultrasound is the primary modality for the evaluation of patients with acute scrotal pathologies (3, 4) and testicular torsion can cause changes in grey-scale, color, and spectral Doppler .Anatomy of the normal testis, bell clapper anomaly and intravaginal testicular torsion. Blue testis, Green epididymis, Lavender spermatic cord and vessels, Red tunica vaginalis. Normally, the epididymis extends along the full length of the testis posterolaterally so that the upper and lower poles of the testis are covered and the tunica vaginalis parietal lamina is anchored to the .
Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. . With the clapper-bell deformity the epididymis, . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that requires multiple hemoclips and . Testicular torsion can be distinguished as two separate mechanisms, extravaginal and intravaginal, depending on whether the torsion includes the tunica vaginalis or occurs within the tunica vaginalis. . Granberg CF, DaJusta DG, Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic Test for Testis Torsion in Pediatric Acute .
testicular torsion vs epididymitis signs
which radiographic test shows soft tissue best
testicular torsion treatment
test for testicular torsion reflex
WEB9 de mar. de 2022 · Quase 2 anos de LPSG e ainda n aprendeu a usar o site? F5 nos horários q terminam em 3, 5 e 7. Nos horários terminados em 3 é 100% de chance de funcionar, se nos terminados em 5 n funcionar, nos 7 funciona, e vice e versa. Exemplo: 13h0 3, 18h0 5, 22h0 7
testicular torsion vs epididymitis test|testicular torsion vs epididymitis signs